The history of buildings
|

|

|

|
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
Buildings have played a significant role in human civilization, reflecting the cultural and social values of different eras, providing shelter and security and adopting and developing technological advancements.
[edit] Ancient architecture
The history of buildings can be traced back to the earliest human civilizations, where people constructed simple structures using natural materials such as wood, animal skins, stone, and clay. These early dwellings were primarily designed to provide shelter and protection from the elements, with little emphasis on aesthetics.
For more information see: Shelter.
However, they quickly developed and became more ornate and complex, with particular styles emerging in different areas depending on the availability of materials, environmental conditions, functional needs, cultural traditions and so on.
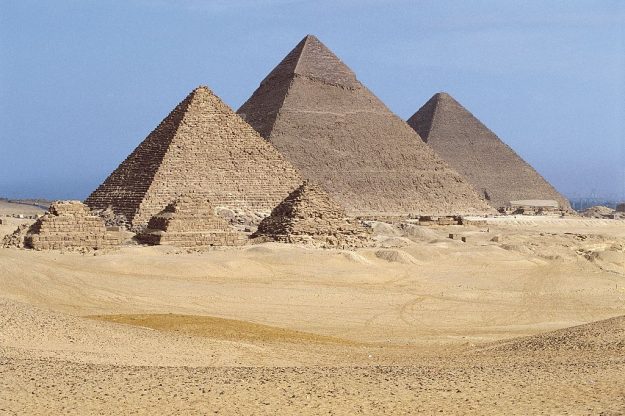
One of the most significant examples of ancient architecture is the Great Pyramid of Giza in Egypt. This monumental structure, built over 4,500 years ago, is a testament to the ingenuity and engineering skills of the ancient Egyptians. The pyramid, which stands over 480 feet tall, was constructed using millions of limestone blocks, each weighing several tons. The pyramid was built as a tomb for pharaohs and their consorts, and was intended to protect their bodies and souls for eternity.
Another example of ancient architecture is the Parthenon in Athens, Greece, built over 2,400 years ago. This temple, dedicated to the goddess Athena, served as the centre of religious and political life in ancient Athens. The Parthenon is renowned for its beautiful architecture and intricate sculptures, which continue to inspire artists and architects to this day.
For more information see: Classical architecture.
[edit] Medieval architecture
During the medieval period, architecture underwent a significant transformation, as new building techniques and materials were developed. Gothic architecture, characterised by its soaring spires, pointed arches, and intricate stone carvings, emerged in France in the 12th century.
One of the most famous examples of Gothic architecture is Notre-Dame Cathedral in Paris, which was built in the 12th and 13th centuries. This stunning cathedral features beautiful stained glass windows, soaring vaulted ceilings, and a towering spire that reaches over 400 feet into the sky. Notre-Dame Cathedral remains one of the most iconic landmarks of Paris and attracts millions of visitors every year.
For more information see: Gothic architecture.
Another significant development in medieval architecture was the construction of castles and fortresses, which served as defensive structures against enemy attacks. One of the most famous examples of a medieval castle is the Tower of London, built in the 11th century by William the Conqueror. The tower has served various purposes throughout history, including as a royal palace, a prison, and a treasury.
For more information see: Medieval architecture.
[edit] Renaissance architecture
During the Renaissance period, architecture underwent another major transformation, as architects began to look back to the classical styles of ancient Greece and Rome for inspiration. Renaissance architecture was characterised by its symmetrical proportions, classical columns, and ornate decoration.
One of the most famous examples of Renaissance architecture is the Palazzo Vecchio in Florence, Italy. This impressive palace, built in the 14th century, served as the seat of government for the city of Florence. The palace features beautiful frescoes, ornate ceilings, and a stunning clock tower that overlooks the city.
Another notable example of Renaissance architecture is St. Peter's Basilica in Vatican City. This iconic structure, designed by Michelangelo, is the largest church in the world and serves as the centre of the Roman Catholic Church. The basilica features a grand dome, towering columns, and beautiful artwork by some of the most renowned artists of the Renaissance period.
For more information see: Renaissance architecture.
[edit] Modern architecture
In the 20th century, architecture underwent another major transformation, as new materials and technologies allowed for the construction of taller and more complex buildings. Modern architecture is characterised by its emphasis on functionality, minimalism, and the use of materials such as steel, concrete, and glass.
One of the most famous examples of modern architecture is the Empire State Building in New York City. Completed in 1931, this iconic skyscraper was the tallest building in the world at the time of its completion, standing at over 1,400 feet tall. The building is renowned for its Art Deco style and has become a symbol of New York City and American architecture.
Another notable example of modern architecture is the Sydney Opera House in Australia. This iconic building, designed by Danish architect Jørn Utzon, is characterised by its distinctive sail-like roofs and has become one of the most recognizable buildings in the world. The Opera House serves as a cultural centre for the city of Sydney and attracts millions of visitors every year.
For more information see: Modern architecture.
[edit] Contemporary architecture
In recent years, architecture has continued to evolve, with architects experimenting with new materials, technologies, and design concepts. Contemporary architecture places an emphasis on sustainability, innovation, and the use of digital tools and techniques.
For example, the Burj Khalifa in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, completed in 2010, is a towering skyscraper stands at over 2,700 feet tall, making it the tallest building in the world. It features a unique design that blends Islamic and contemporary architectural styles, and it serves as a symbol of Dubai's modernisation and economic growth.
Another example of contemporary architecture is the Heydar Aliyev Center in Baku, Azerbaijan. Designed by architect Zaha Hadid, the centre has flowing curves and an organic forms and serves as a cultural centre for the city of Baku.
[edit] Conclusion
The history of buildings is a testament to human creativity, ingenuity, and innovation. From the simple dwellings of our ancient ancestors to the towering skyscrapers of today, architecture has evolved in response to changing cultural, social, and technological trends. The buildings of the past continue to inspire and captivate us, while the buildings of the present and future push the boundaries of what is possible.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Architectural design.
- Architectural styles.
- Art Deco.
- Arts and craft movement.
- Bauhaus.
- Brutalism.
- Building Construction in Britain from 600AD to 1890.
- De Stijl.
- English architectural stylistic periods.
- High-tech architecture.
- International Style.
- Medieval architecture.
- Modernist architecture.
- Nineteenth century architecture.
- Postmodern architecture.
- Shelter.
- Types of building.
- Vernacular architecture.
Featured articles and news
Call for greater recognition of professional standards
Chartered bodies representing more than 1.5 million individuals have written to the UK Government.
Cutting carbon, cost and risk in estate management
Lessons from Cardiff Met’s “Halve the Half” initiative.
Inspiring the next generation to fulfil an electrified future
Technical Manager at ECA on the importance of engagement between industry and education.
Repairing historic stone and slate roofs
The need for a code of practice and technical advice note.
Environmental compliance; a checklist for 2026
Legislative changes, policy shifts, phased rollouts, and compliance updates to be aware of.
UKCW London to tackle sector’s most pressing issues
AI and skills development, ecology and the environment, policy and planning and more.
Managing building safety risks
Across an existing residential portfolio; a client's perspective.
ECA support for Gate Safe’s Safe School Gates Campaign.
Core construction skills explained
Preparing for a career in construction.
Retrofitting for resilience with the Leicester Resilience Hub
Community-serving facilities, enhanced as support and essential services for climate-related disruptions.
Some of the articles relating to water, here to browse. Any missing?
Recognisable Gothic characters, designed to dramatically spout water away from buildings.
A case study and a warning to would-be developers
Creating four dwellings... after half a century of doing this job, why, oh why, is it so difficult?
Reform of the fire engineering profession
Fire Engineers Advisory Panel: Authoritative Statement, reactions and next steps.
Restoration and renewal of the Palace of Westminster
A complex project of cultural significance from full decant to EMI, opportunities and a potential a way forward.
Apprenticeships and the responsibility we share
Perspectives from the CIOB President as National Apprentice Week comes to a close.






















Comments
[edit] To make a comment about this article, or to suggest changes, click 'Add a comment' above. Separate your comments from any existing comments by inserting a horizontal line.